Thyroid tests are critical diagnostic tools used to evaluate the function of the thyroid gland, a small but significant organ located in the neck. The thyroid gland produces hormones that regulate metabolism, energy production, and overall body function. Imbalances in thyroid hormone levels can lead to various health problems, making thyroid tests essential for early detection and effective management of thyroid disorders. In this article, we will explore the types of thyroid test, their importance, and what to expect during the testing process.
Importance of Thyroid Tests
- Early Detection of Disorders: Thyroid tests can identify imbalances in thyroid hormone levels, allowing for early diagnosis and treatment of conditions like hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism.
- Monitoring Treatment: For individuals already diagnosed with thyroid conditions, regular tests help monitor the effectiveness of treatment and make necessary adjustments.
- Overall Health Assessment: Thyroid function affects various body systems. Regular testing ensures any thyroid-related health issues are promptly addressed.
Types of Thyroid Tests
Several tests are available to assess thyroid function. The most common ones include:
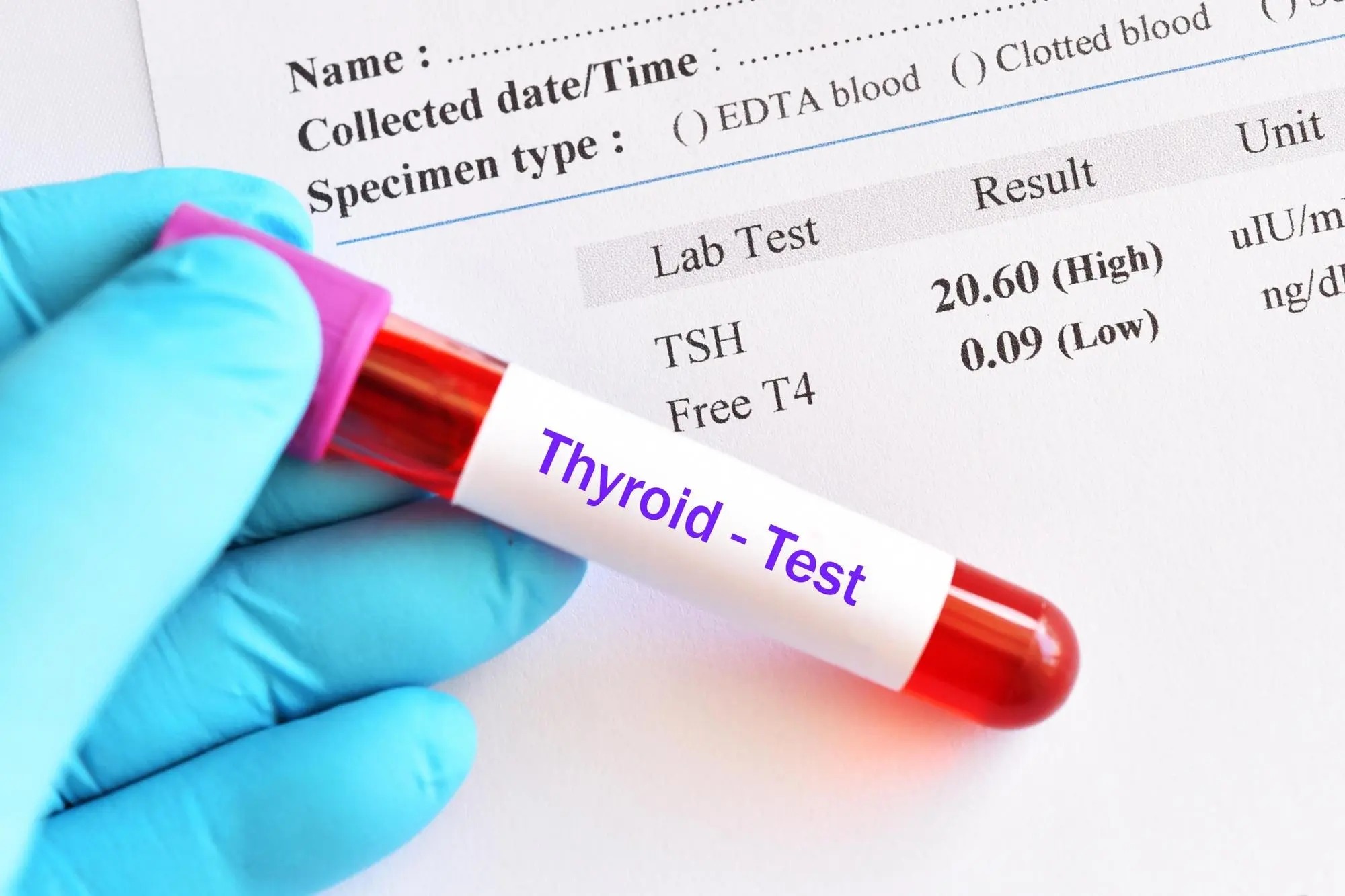
- TSH (Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone) Test: Measures the level of TSH in the blood. Elevated TSH levels may indicate hypothyroidism, while low levels may suggest hyperthyroidism.
- T3 and T4 Tests: Measure the levels of triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4) hormones. These tests help determine whether the thyroid is producing the right amount of hormones.
- Free T3 and Free T4 Tests: Measure the unbound, active forms of T3 and T4. These tests provide a more accurate assessment of thyroid hormone activity.
- Thyroid Antibody Tests: Detect the presence of antibodies that may indicate autoimmune thyroid conditions such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis or Graves’ disease.
- Thyroid Ultrasound: Uses sound waves to create images of the thyroid gland, helping to detect nodules, cysts, or other abnormalities.
- Radioactive Iodine Uptake Test: Measures how much iodine the thyroid gland absorbs from the blood, which can help diagnose hyperthyroidism and other conditions.
What to Expect During a Thyroid Test
Thyroid tests are generally straightforward and involve minimal discomfort. Here’s what to expect for the most common tests:
- Blood Tests: A healthcare professional will draw a small sample of blood from a vein in your arm. The process is quick and usually takes just a few minutes.
- Ultrasound: You will lie on an examination table, and a technician will apply a gel to your neck and use a transducer to capture images of the thyroid gland. The procedure is painless and typically takes about 30 minutes.
- Radioactive Iodine Uptake Test: You will swallow a small amount of radioactive iodine, either in a capsule or liquid form. Later, a special camera measures how much iodine the thyroid absorbs. This test may require multiple visits over a day or two.
Interpreting Thyroid Test Results
Understanding thyroid test results can be complex, and it’s essential to discuss them with your healthcare provider. Generally:
- Normal Results: Indicate that your thyroid is functioning properly.
- Abnormal TSH Levels: High TSH suggests hypothyroidism, while low TSH indicates hyperthyroidism.
- Abnormal T3 and T4 Levels: Can confirm hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism and help determine the severity of the condition.
- Presence of Antibodies: May indicate autoimmune thyroid diseases.
When to Get a Thyroid Test
Thyroid tests are particularly useful in the following scenarios:
- Routine Check-ups: Part of regular health screenings to monitor thyroid function.
- Symptoms of Thyroid Imbalance: If you experience symptoms such as fatigue, weight changes, hair loss, or changes in heart rate.
- Family History: If you have a family history of thyroid disorders, regular testing can help in early detection.
- Existing Thyroid Conditions: Monitoring the effectiveness of treatment and making necessary adjustments.
Benefits of Regular Thyroid Testing
Regular thyroid testing offers numerous benefits:
- Early Intervention: Helps in the early detection and management of thyroid conditions, reducing the risk of complications.
- Treatment Adjustment: Enables healthcare providers to adjust medications and treatment plans effectively.
- Health Maintenance: Ensures that thyroid hormone levels are within a normal range, contributing to overall health.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Provides insights into how lifestyle factors, such as diet and stress, affect thyroid function.
Conclusion
Thyroid tests are vital for maintaining thyroid health and overall well-being. Whether you’re experiencing symptoms of thyroid imbalance or monitoring an existing condition, these tests provide essential insights into thyroid function. Regular testing and consultation with a healthcare provider ensure that any thyroid-related issues are promptly addressed, helping you maintain a healthy and active life. Prioritize your thyroid health by scheduling regular thyroid tests and discussing the results with your doctor.