Overview
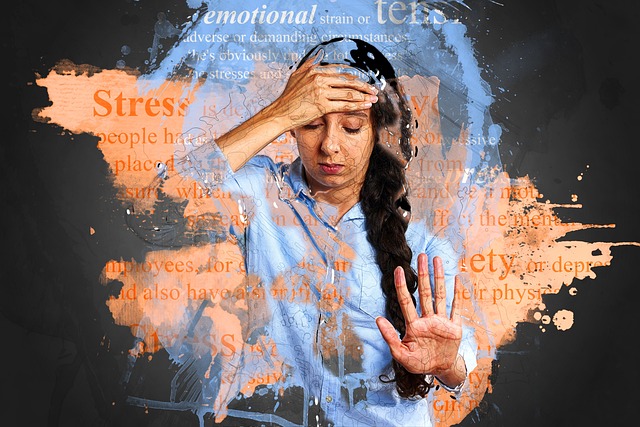
With its widespread presence and diverse manifestations, anxiety can seem like an overwhelming obstacle to many people. But managing anxiety requires a mix of doable fixes and therapeutic understandings that enable people to take control of their symptoms and enhance their quality of life. We examine useful coping mechanisms and therapeutic insights for anxiety in this extensive guide, providing a path to resilience and wellbeing.
Recognizing Anxiety: A Complicated Environment
Anxiety is a complex disorder that manifests as a variety of symptoms, including physical tension, panic attacks, and ongoing concern and terror. It is essential to comprehend the underlying reasons and triggers of anxiety disorder in order to create efficient coping mechanisms that deal with the core of the issue.
Realistic Coping Techniques:
Instruments for Everyday Life
Breathing Techniques:
Diaphragmatic breathing and the 4-7-8 technique are two deep breathing techniques that assist trigger the body’s relaxation response and lessen anxiety symptoms. People can control their breathing patterns and encourage emotions of peace and relaxation by concentrating on taking slow, deep breaths.
By bringing attention to the present moment without passing judgment, mindfulness meditation enables people to accept and show compassion for their thoughts and feelings. Regular mindfulness practice can help people feel less anxious and be better able to handle stress.
Tensing and then relaxing each muscle group in the body, starting with the toes and working your way up to the head, is known as progressive muscle relaxation, or PMR. Through methodically releasing bodily tension, people can encourage relaxation and lessen their anxiety symptoms.
Cognitive-Behavioral Methods: Reorganizing Mental Processes
Cognitive Restructuring: This technique entails recognizing and combating unfavorable cognitive processes that fuel worry. People can alter their perspective of frightening circumstances and lower their anxiety levels by swapping out distorted or unreasonable thoughts for more accurate and balanced ones.
Exposure Counseling: In a safe and controlled environment, patients undergoing exposure treatment are gradually exposed to stimuli or situations that they dread. People can lessen avoidance tendencies and increase their confidence in their ability to cope with anxiety by facing their worries and realizing that they can handle discomfort without feeling harm.
Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT): ACT helps people resolve to doing things that are consistent with their values while accepting their thoughts and feelings without passing judgment. With the support of psychological flexibility and resilience, Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) helps people live less anxious lives and achieve meaningful goals.
Lifestyle Changes:
Developing Well-Being Frequent Exercise: Research has shown that exercise, which releases endorphins and encourages relaxation, can lessen the symptoms of anxiety and depression. Regular exercise, like jogging, yoga, or walking, can help people reduce stress and enhance their general mood and well-being.
Good Sleep Practices:
Emotional stability and mental well-being depend on getting enough sleep. Enhancing sleep quality and lowering anxiety symptoms can be achieved by adopting appropriate sleep hygiene practices, such as sticking to a regular sleep schedule, setting up a calming bedtime ritual, and avoiding stimulants just before bed.
Stress Management Techniques:
Reducing the symptoms of anxiety requires a thorough understanding of efficient stress management. People can manage stressors more skillfully and keep them from becoming overwhelming by using strategies like time management, relaxation, and boundary establishing.
Healing Perspectives: Recognizing the Fundamental Dynamics
Psychoeducation: Acknowledging the physiological and psychological aspects of anxiety and its nature can enable people to take charge of their symptoms and seek the right care. Psychoeducation aids in the identification of anxiety symptoms and the development of appropriate coping mechanisms.
Investigating the Causes: Anxiety is frequently caused by psychological or emotional problems that need to be investigated and resolved. In order to identify and treat these underlying causes, therapy can offer people a secure and encouraging environment, which can result in long-term relief from anxiety symptoms.
Developing Resilience To be resilient is to have the capacity to adjust to and overcome hardship. Through coping skill instruction, the development of self-awareness and self-compassion, and the encouragement of a sense of empowerment and control over worry, therapy can assist people in becoming more resilient.
In summary
Anxiety management is a complex process that calls for a blend of therapeutic ideas and useful coping mechanisms. People can effectively manage their symptoms and regain control of their lives by adding deep breathing exercises, mindfulness meditation, cognitive-behavioral strategies, lifestyle modifications, and therapy insights to their repertoire of coping mechanisms. Let’s embrace helpful strategies and therapeutic insights to manage anxiety and promote wellbeing and resilience in the face of hardship.